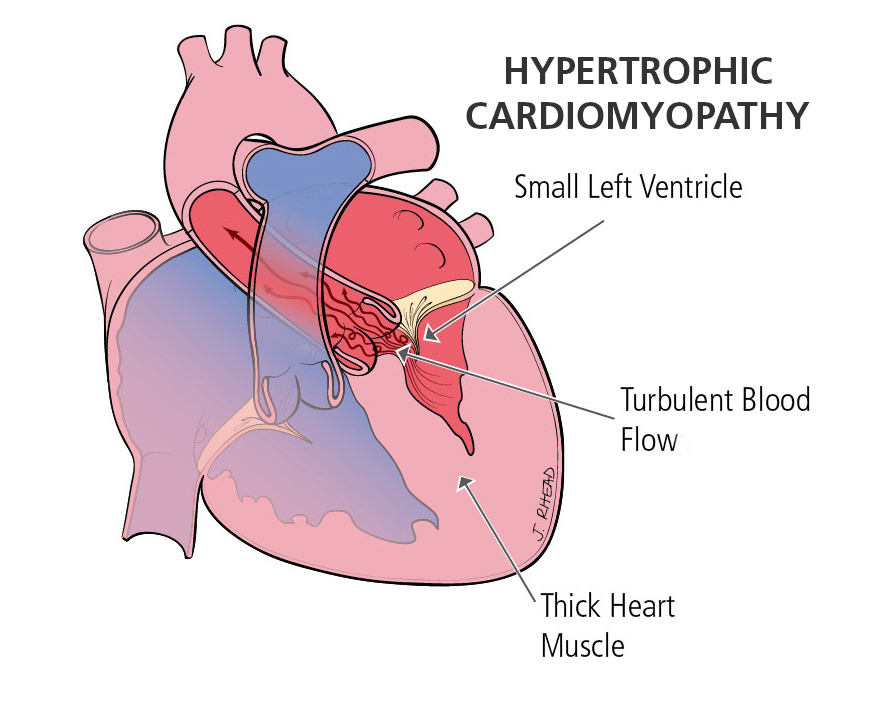
What exactly is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HSM)? Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathies (HCM), also referred to as familial myopathies, is a family of inherited diseases which affects the cardiac muscles and tissue. It is passed down through the genes. The other terms often used to describe this condition are idiopathic hypertrophy subventricular tachycardia (IHSTC) and hypertrophagic sub ventricular tachycardia (HSCTC).
Myopathy refers to the process by which a part of the heart produces abnormally high amounts of potassium
Potassium in the body controls the functioning of the cardiac muscles. Hypertrophy, or excessive growth, of cardiac muscles is caused by abnormal production of potassium in the tissues. Hypertrophy, or excess growth, of cardiac muscle tissues is known as hyperkalemia. Hypertrophy is known to be associated with a number of serious diseases, including congestive heart failure and myocardial infarction.
What are the symptoms of myopathy? The most common symptoms of myopathy include a fast, pounding, short-tempered heartbeat, rapid and irregular heart beat, heart palpitations, and breathlessness. People with myopathy can experience sudden death from heart attack or arrhythmia without warning. People with myopathy may have symptoms that are consistent with atrial fibrillation but there may be no chest pain or flutter and no apparent reason for the fast beating heart. A family history of cardiac problems, high blood pressure, heart failure, or other heart diseases may increase the risk of having hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Does myopathy affect the other major risk factors of heart disease, such as smoking, hypertension and coronary artery disease? Smoking, hypertension, and coronary artery disease are known to increase the risk of myopathy. Hypertrophy of the heart muscles is more likely to occur in people who are overweight, are smokers, and have coronary artery disease or heart disease. Studies indicate that men who smoke, have high blood pressure, have a family history of cardiovascular diseases, and have coronary artery disease are at increased risk for having myopathy.
Does family history of myopathy affect the risk of having IHSTC or HSC? People who have a sibling with this condition are at a greater risk of having IHSTC than people with a non-familial form of myopathy, such as familial myopathies caused by genetic inheritance.
Are there any medical tests to help diagnose myopathy? There are no tests available to diagnose this condition. However, most people with myopathy are referred to a cardiologist who can perform laboratory tests that will rule out potential causes of IHSTC and HSC. This involves a detailed physical examination of the heart.
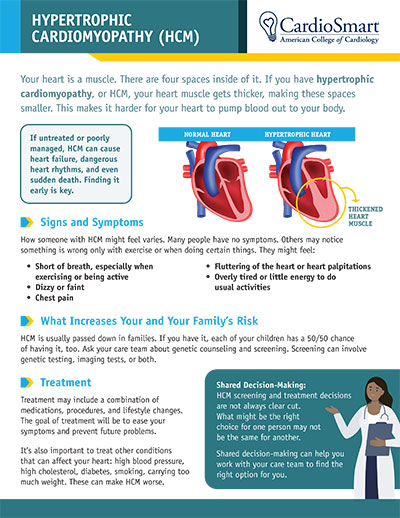
How is myopathy treated?
There are several ways in which treatment of myopathy can occur. The most common treatment consists of a combination of medications that target heart muscles that have abnormal growth. In addition, other treatments can include surgery and exercise.
Is there a cure for myopathy? While there is currently no known cure for this condition, the treatment options are often similar to those used for coronary heart disease. The goal of treatment is to keep the myocardium from growing abnormally and to slow down the heart rate so that the heart does not overwork itself.
Is myopathy dangerous? This is a question that many people who suffer from this condition ask. They fear that they may have increased the risk of heart attacks and heart failure. While there is no evidence to suggest that this is the case, if you do suffer from myopathy, it is important to speak to your doctor about possible treatment options.
How is myopathy diagnosed? Most people who have this condition will be referred to a cardiologist who will conduct laboratory tests and perform imaging studies, such as X-rays, echocardiography and cardiogenic shock.
What are some of the treatments for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? If you are worried that you may have this condition, it is important to contact a cardiologist. to discuss options to treat your condition.
It is also important to note that some patients with this condition are prescribed medication such as aspirin and other beta blockers. While it is impossible to prevent, the best thing that you can do is to take good care of your health.